Rheumatology focuses on diagnosing and treating autoimmune and inflammatory diseases that primarily affect joints, muscles, and connective tissues.
Accurate CPT coding is vital in this specialty to ensure proper documentation of procedures, timely reimbursements, and seamless patient care.
This article delves into the most commonly used CPT codes in rheumatology for various diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
What Are CPT Codes in Rheumatology?
CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) codes are a standardized system used to document medical services and procedures. These codes streamline the billing process, improve communication between healthcare providers and insurers, and ensure accurate reimbursement for services rendered.
In rheumatology, CPT codes cover a wide range of services, including joint injections, diagnostic imaging, lab tests, and consultations. Providers rely on these codes to track treatments and monitor patient outcomes effectively.
Commonly Used CPT Codes in Rheumatology
Here’s an overview of the most frequently utilized CPT codes in rheumatology practices:
99213 – Established Patient Office Visit
CPT code 99213 is one of the most frequently used in rheumatology. It represents an office visit for an established patient involving a low level of medical decision-making. This code is often used during follow-ups for chronic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis (RA), lupus, and osteoarthritis, where rheumatologists monitor disease progression and adjust treatment plans. Considering that RA affects over 18 million people worldwide, such visits are crucial for maintaining disease control and improving patient outcomes.
20610 – Aspiration or Injection of Major Joint
The 20610 CPT code is used for aspiration or injection into a major joint, such as the knee, shoulder, or hip. This procedure is a cornerstone of rheumatology practice, commonly performed to relieve pain, administer corticosteroids, or collect synovial fluid for diagnostic purposes. It is particularly beneficial for managing conditions like gout, psoriatic arthritis, and advanced RA, where joint inflammation leads to significant discomfort and functional limitations.
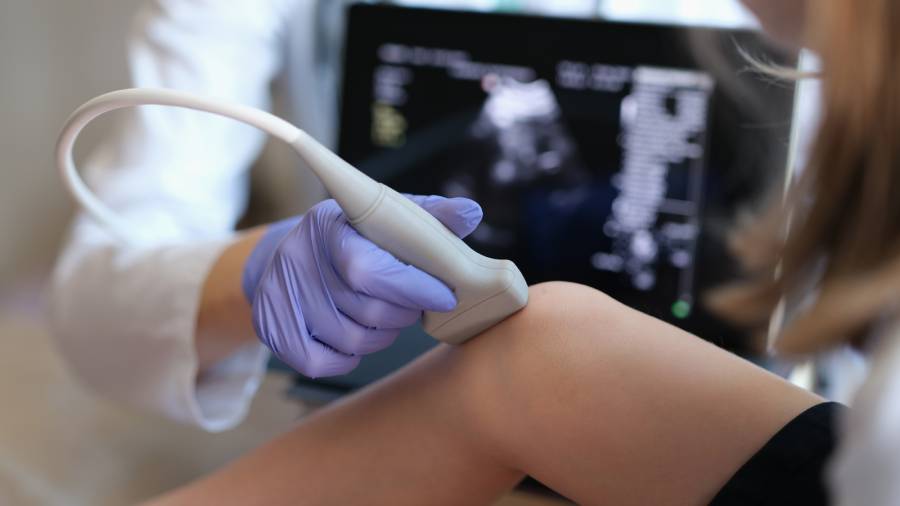
20611 – Joint Injection with Ultrasound Guidance for Rheumatoid Arthritis
CPT code 20611 is used for joint injections with ultrasound guidance, improving accuracy and reducing complications. This is particularly beneficial for patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), which affects approximately 1.3 million Americans and causes joint inflammation in areas like the knees, shoulders, and hands. Ultrasound helps target hard-to-reach joints, ensuring more precise injections for pain relief, reduced inflammation, and improved mobility in RA patients.
76881 – Complete Joint Ultrasound
CPT code 76881 is used for a comprehensive ultrasound examination of joints and surrounding soft tissues. This diagnostic imaging method is invaluable for assessing inflammation, joint damage, or synovial abnormalities in conditions like RA and lupus. Complete ultrasounds help rheumatologists evaluate the extent of disease progression, particularly in patients experiencing persistent or unexplained symptoms.
76882 – Limited Joint Ultrasound
For targeted assessments, CPT code 76882 is used to document limited joint ultrasounds that focus on a specific area within a joint.
This procedure is often employed for diagnosing localized inflammation, tendon injuries, or joint effusion. It complements other diagnostic tools, providing detailed insights into the underlying causes of pain and swelling.
85652 – Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Test
The ESR test, coded as 85652, measures the rate at which red blood cells settle in a tube of blood over an hour. This is a key indicator of inflammation and is commonly ordered for patients suspected of having autoimmune diseases like RA or vasculitis. Elevated ESR levels often correlate with active disease states, guiding rheumatologists in determining treatment efficacy or disease progression. For instance, the annual incidence of ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) is approximately 1.2 to 2.0 per 100,000 individuals, with a prevalence of 4.6-18.4 per 100,000. The ESR test is crucial in monitoring the inflammation associated with these conditions and helping guide treatment decisions.
86140 – C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Test
CPT code 86140 is used for the C-reactive protein (CRP) test, another marker of inflammation. CRP levels tend to rise during flare-ups of autoimmune conditions, making this test essential for tracking the severity of diseases like RA and ankylosing spondylitis. The widespread use of CRP testing underscores its importance in tailoring treatment regimens to individual patient needs.
36415 – Venous Blood Collection
CPT code 36415 documents the collection of venous blood by venipuncture. Blood tests are integral to diagnosing and managing autoimmune conditions, as they help measure inflammation markers, antibodies, and other critical parameters. Accurate coding of blood collection ensures proper reimbursement for this routine but essential procedure in rheumatology practices.
The Importance of Accurate CPT Coding in Rheumatology
Accurate CPT coding is a cornerstone of successful rheumatology practice management. It ensures:
- Timely and Accurate Reimbursements: Proper documentation minimizes claim denials and billing errors, helping practices maintain a steady cash flow.
- Streamlined Patient Care: Precise coding supports efficient tracking of treatments, enabling healthcare providers to monitor patient progress and adjust care plans effectively.
- Regulatory Compliance: Staying updated with the latest CPT codes helps providers adhere to industry standards, reducing the risk of penalties and audits.
Mastering CPT coding not only benefits administrative processes but also enhances the overall quality of care delivered to patients.

Conclusion
CPT codes play a pivotal role in rheumatology, from documenting consultations to billing for complex procedures like joint injections and ultrasounds. By mastering the use of these codes, healthcare providers can improve patient care, optimize reimbursements, and minimize administrative challenges.For practices overwhelmed by the complexities of medical coding, partnering with rheumatology billing services can help ensure accuracy and efficiency. Such services handle the intricate coding and billing processes, allowing providers to focus on delivering quality care while improving their revenue cycle management.

With a strong background in the marketing industry and healthcare leadership roles, Filip is responsible for CLICKVISIONBPO’s sales strategies and onboarding new clients. With a passion for sharing insights gained from his experience, he also shares valuable knowledge through industry related articles.
